You are implementing a new frame relay network to provide connectivity between you offices. To do this, you set up the frame relay network using point-to-point subinterfaces.
Which of the following does NOT need to be configured?
A. The Frame Relay encapsulation on the physical interface.
B. The local DLCI on each subinterface.
C. An IP address on the physical interface.
D. The subinterface type as point-to-point.
Explanation:
When using point to point subinterfaces in a frame relay network, the subinterfaces will each have their own IP addresses and will each be contained within their own IP subnet.
The physical interface does not require an IP address.
Incorrect Answers:
A. The physical interface will need to be configured with a layer two encapsulation type, so in this case it must be frame relay.
B. The subinterfaces will have the local DLCI assigned to each one, using the "frame-relay interface-dlci" command for each of the subinterfaces.
D. Each subinterface should be configured as a point to point network type.
QUESTION 112:

After the router interfaces shown in the diagram have been configured, it is discovered that hosts in the Branch LAN cannot access the Internet.
Further testing reveals additional connectivity issues.
What will fix this problem?
A. Change the address of the Branch router LAN interface.
B. Change the address of the Branch router WAN interface.
C. Change the subnet mask of the HQ router LAN interface.
D. Change the address of the HQ router LAN interface.
E. Change the address of the HQ router interface to the Internet.
F. Change the subnet mask of the HQ router interface to the Internet.
Explanation:
The serial line connection between the Branch office and the HG office should have interfaces that belong in the same subnet. Based on the diagram above, the WAN interface of the Branch router is configured with an IP address that is in a different IP network than the serial interface of the HG router. As it is set up currently, no traffic will pass from the Branch router to the HG until these two interfaces are in the same subnet.
QUESTION 113:
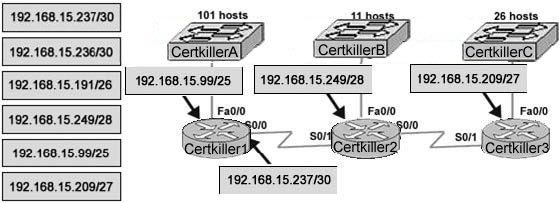
A portion of he Certkiller network is shown in the diagram below:

Consider the 192.1.1.0/24 network in this exhibit. This network uses RIP v2.
Which combination of subnetwork assignments will satisfy the requirements for networks A, B, and C of this design? (Select three)
A. Network A = 192.1.1.128/25
B. Network A = 192.1.1.0/25
C. Network B = 192.1.1.252/30
D. Network B = 192.1.1.4/30
E. Network C = 192.1.1.64/26
F. Network C = 192.1.1.224/27
Explanation:
To properly answer this question, it is best to start from the end, which is network C.
Since network C requires at least 55 host addresses, a /26 network must be used. A network mask of /26 will provide for 62 usable IP addresses while a /27 network will only provide for 30 so we must choose E. With choice E taken, hosts within the range of 192.1.1.65-192.1.1.126 will be used.
For network A, both choices A and B are using the correct subnet mask, but we are only limited to choice A since many of the hosts in choice B are already being used in network C. Finally, for network B we are left with choice D since hosts in choice C are already being used by network A.
QUESTION 114:

Assume that RIP v1 is the only routing protocol in use. What is the Maximum number of usable IP address that can be supported on each LAN if the Certkiller network is using one Class C address block?
A. 14
B. 16
C. 30
D. 32
E. 62
F. 64
Explanation:
RIP version 1 does not support VLSM information, so all networks must have the same subnet mask. In the network above, there are a total of 12 networks (6 LANs and 6 different point to point WAN connections). Therefore, if each of the 12 networks use the 255.255.255.240 subnet mask, there will be a total of 16 networks with 14 usable hosts on each LAN.
Incorrect Answers:
C, E: These options will not provide enough separate networks. A total of 12 are required due to the use of a protocol that does not support VLSM.
D, F. These options omit the fact that we must subtract 2 addresses from the usable range for the network and broadcast IP addresses for each subnet.
QUESTION 115:
You are a technician at Certkiller . Your newly appointed Certkiller trainee wants to know what the CDP is.
What would your reply be? (Choose all that apply.)
A. It is globally enabled by default on Cisco routers.
B. It is globally enabled by default on all routers.
C. It is a proprietary protocol.
D. It is a non-proprietary protocol.
E. It can be used to gather hardware and protocol information about neighbor devices.
Explanation:
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol designed to help administrators collect information about local and remote devices. You can use the CDP to gather hardware and protocol information about neighbor devices, which can be useful for troubleshooting and documenting the network.
The CDP discovers basic information about neighboring routers and switches, without needing to know the passwords for the neighboring devices. CDP supports any LAN, HDLC, Frame Relay, and ATM interface- in fact; it supports any interface that supports the use of SNAP headers. The router or switch can discover Layer 2 and layer 3 addressing details of neighboring router without even configuring that Layer 3 protocol - this is because CDP is not dependant on any particular Layer 3 protocol.
QUESTION 116:
Five different routers are connected via varying point to point circuit types as displayed below:

Which of the following statements are true regarding how router A will chose a path to router E? (Choose three)
A. If RIP is the routing protocol, router A will determine all paths have an equal cost.
B. If RIP is the routing protocol, router A will install only the ADE path in its routing table.
C. If IGRP is the routing protocol, router A will determine that path ACE has the lowest cost.
D. If IGRP is the routing protocol, router A will determine that path ADE has the lowest cost.
E. If RIP and IGRP are both configured on router A, the router will use the route information learned by IGRP.
F. If RIP and IGRP are both configured on router A, the router will use the route information learned by RIP.
Explanation:
RIP simply uses hop counts as the metric for path determination, so RIP will see all routes as equal in this case. IGRP uses bandwidth and delay, by default, so it will prefer the paths over the T3 links. By default, IGRP routes are always preferred over RIP routes because IGRP has a lower Administrative Distance (AD) than RIP. The AD of IGRP is 100 while the AD of RIP is 120.
QUESTION 117:
You work as a network engineer at Certkiller .com. You are required to allow establishment of a Telnet session with a router Certkiller C.
Which set command must be configured?
A. Certkiller C(config)# line console 0
Certkiller C(config-line)# enable password Certkiller
B. Certkiller C(config)# line console 0
Certkiller C(config-line)# enable secret Certkiller
Certkiller C(config-line)# login
C. Certkiller C(config)# line console 0
Certkiller C(config-line)# password Certkiller
Certkiller C(config-line)# login
D. Certkiller C(config)# line vty 0
Certkiller C(config-line)# enable password Certkiller
E. Certkiller C(config)# line vty 0
Certkiller C(config-line)# enable secret Certkiller
Certkiller C(config-line)# login
F. Certkiller C(config)# line vty 0
Certkiller C(config-line)# password Certkiller
Certkiller C(config-line)# login
Explanation:
CLI Password Configuration:

QUESTION 118:
The Certkiller WAN is depicted below:

As a network technician at Certkiller .com you would like to implement NAT in the network shown in the exhibit. You would like to allow inside hosts to use a private addressing scheme. Where should NAT be configured?
A. Certkiller 1 router
B. Certkiller 2 router
C. Certkiller 3 router
D. All routers
E. All routers and switches
Explanation:
NAT should always be configured on the border device. It can be a either a border router or a PIX firewall connecting to the Internet.
QUESTION 119:
Which command will configure a default route on a router?
A. router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.1
B. router(config)# ip default-route 10.1.1.0
C. router(config)# ip default-gateway 10.1.1.0
D. router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1
Explanation:
The command "IP route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Incorrect Answers:
A. This will be an invalid route, since the "10.1.1.0" value will specify the network mask, which in this case is invalid.
B, C. These commands are invalid. The command "ip default-network" could be used, but not "ip default-route" or "ip default-gateway". IP default-gateway is used on switches, not routers.
QUESTION 120:
In which situation would the use of a static route be appropriate?
A. To configure a route to the first Layer 3 device on the network segment.
B. To configure a route from an ISP router into a corporate network.
C. To configure a route when the administrative distance of the current routing protocol is too low.
D. To reach a network is more than 15 hops away.
E. To provide access to the Internet for enterprise hosts.
Explanation:
Static routes are special routes that the network administrator manually enters into the router configuration. Stub networks are the ideal candidate for static routes.
There is no need to run a routing protocol over the WAN links between an ISP Router and a corporate network when only a single Internet link exists.
QUESTION 101:
See the Certkiller WAN diagram below:
Certkiller has four offices, each with its own network, as shown in the graphic. Three of the networks have approximately 50 hosts each, and one network has 10 hosts.
The multi-vendor routers are connected by serial links that use separate subnetwork numbers. The Certkiller network has leased one Class C address to be used for all networks and serial links, and they do not wish to replace any of their existing routers.
Which routing protocol would be most appropriate for this scenario?
A. TCP/IP
B. RIP version 1
C. RIP version 2
D. IGRP
E. EIGRP
F. All of the above are acceptable
Explanation:
The question describes 2 important requirements. The first is the fact that a routing protocol that supports VLSM is needed, as specified by the fact that one class C address range is to be used for all networks. The second important requirement is that routers from multiple vendors are being used, so the routing protocol chosen must be non-proprietary. RIP version 2 is a standards based routing protocol that supports variable length subnet masking (VLSM). Note that OSPF would also be a viable choice, but it was not one of the answer choices.
Incorrect Answers:
A. This is not a routing protocol.
B. RIP version 1 does not support VLSM
D, E: Although these both support VLSM, IGRP and EIGRP are Cisco proprietary routing protocols which are not supported by other router vendors.
QUESTION 102:
RIP version 2 is being used as the routing protocol within the Certkiller network.
What does RIP version 2 use to prevent routing loops? (Choose two)
A. CIDR
B. Split horizon
C. Authentication
D. Classless masking
E. Hold-down timers
F. Multicast routing updates
G. Path Vectoring
Explanation:
Distance Vector routing protocols employ the split horizon mechanism to reduce the possibility of routing loops. Split horizon blocks information about routes from being advertised by a router out of any interface from which that information originated.
RIP versions 1 and 2 also use the concept of hold timers. When a destination has become unreachable (or the metric has increased enough to cause poisoning), the destination goes into "holddown". During this state, no new path will be accepted for the same destination for this amount of time. The hold time indicates how long this state should last.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C, D, F. Although these are all features and functions of RIP version 2, they are not mechanisms used to prevent routing loops.
G. Path Vectoring is a concept used by BGP routers. RIP version 1 and 2 are considered to be distance vector routing protocols.
QUESTION 103:
The Certkiller WAN is displayed in the diagram below:
A. RIP v1
B. RIP v2
C. IGRP
D. OSPF
E. BGP
F. EIGRP
Explanation:
the exhibit showed routers withVariable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM), and asked which 3 protocols can be used. 3 protocols that support VLSM are RIP v2, OSPF and EIGRP.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: Both of these routing protocols do not support VLSM information.
E. BGP is used for external routing between different autonomous systems, and is not generally used within a single AS.
QUESTION 104:
The Certkiller Network consists of the following 5 IP networks:
NETWORK 1: 192.168.10.0/26
NETWORK 2: 192.168.10.64/27
NETWORK 3: 192.168.10.96/27
NETWORK 4: 192.168.10.128/30
NETWORK 5: 192.168.10.132/30
Which of the following routing protocols will support this IP addressing scheme?
(Choose all that apply).
A. RIP version 1
B. RIP version 2
C. IGRP
D. EIGRP
E. OSPF
F. BGP
Explanation:
Because this network is using IP subnets with variable length subnet masks, only routing protocols that support VLSM will fit this particular case. The routing protocols that support VLSM are RIP v2, EIGRP and OSPF.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: RIP version 1 and IGRP do not support VLSM information within the routing updates.
F. BGP is used for inter-AS routing, such as the Internet. It is not normally used as an
Interior routing protocol.
QUESTION 105:
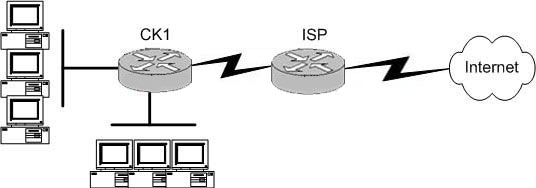
The Certkiller network is displayed in the diagram shown below:
The Certkiller network consists of a small office with twenty-five employees that has one connection to the Internet through the CK1 router. What routing configurations are recommended on the CK1 and ISP routers?
A. BGP on both the routers.
B. RIP on both the routers.
C. Default routes on both routers.
D. BGP on the ISP router and a static route on CK1 .
E. A default route on CK1 and a static route on the ISP router.
Explanation:
Since private network use RFC 1918 IP address ranges internally, and because of security reasons, it is generally not possible to use an interior routing protocol with the ISP. This eliminates choice B. When connecting to an ISP, usually only BGP or static routes are supported. In this case, since there is only one connection to the Internet, BGP is not needed so choices A and D can be eliminated. A static default route would be needed on router CK1 to route to the Internet. In turn, the ISP only needs a specific static route to reach the LAN of the Certkiller network.
Incorrect Answers:
A, D: BGP is not needed on networks that contain only a single link to the Internet.
B. Interior routing protocols are generally not supported with an ISP.
C. A default route on the ISP router would send all of their customers Internet traffic to the Certkiller network, and not the Internet.
QUESTION 106:
What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR election?
A. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which OSPF router will become the DR or BDR in a point-to-point network
B. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which interface will be used to form a neighbor relationship with another OSPF router
C. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which router will become the DR or BDR in a multi access network
D. It is used to determine which interfaces will send Hello packets to neighboring OSPF routers
Explanation:
The router ID is the highest IP address or the highest IP address among loopback addresses (if one is configured) on the Cisco router or can be configured manually by "router-id x.x.x.x". Once the router ID is chosen, it will not be changed unless the OSPF process is reset(clear ip ospf process xx) or the router is reloaded. The IP address of router ID doesn't need to be reachable, but it is used to determine which will router will become the DR or BDR in a multi-access network.
QUESTION 107:
The Certkiller network is shown in the following exhibit:
Which routing protocols can be used within the enterprise network shown in the diagram? (Choose three.)
A. RIP v1
B. RIP v2
C. IGRP
D. OSPF
E. BGP
F. EIGRP
Explanation:
In this network there are IP subnets which use variable length subnet masks. RIP V2,
OSPF and EIGRP are the interior routing protocols that support VLSM.
QUESTION 108:
What is the advantage of using a multipoint interface instead of point-to-point subinterfaces when configuring a Frame Relay hub in a hub-and-spoke topology?
A. It avoids split-horizon issues with distance vector routing protocols.
B. IP addresses can be conserved if VLSM is not being used for subnetting.
C. A multipoint interface offers greater security compared to point-to-point subinterface configurations.
D. The multiple IP network addresses required for a multipoint interface provide greater addressing flexibility over point-to-point configurations.
Explanation:
Frame Relay supports two types of interfaces: point-to-point and multipoint. The one you choose determines whether you need to use the configuration commands that ensure IP address to data-link connection identifier (DLCI) mappings. After configuring the PVC itself, you must tell the router which PVC to use in order to reach a specific destination.
Let's look at these options:
1. Point-to-point subinterface - With point-to-point subinterfaces, each pair of routers has its own subnet. If you put the PVC on a point-to-point subinterface, the router assumes that there is only one point-to-point PVC configured on the subinterface. Therefore, any IP packets with a destination IP address in the same subnet are forwarded on this VC. This is the simplest way to configure the mapping and is therefore the recommended method.
Use the frame-relay interface-dlci command to assign a DLCI to a specified Frame
Relay subinterface.
2. Multipoint networks - Multipoint networks have three or more routers in the same subnet. If you put the PVC in a point-to-multipoint subinterface or in the main interface (which is multipoint by default), you need to either configure a static mapping or enable inverse Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) for dynamic mapping.
QUESTION 109:
Certkiller .com is merging with several local businesses that use routers from multiple vendors. Which routing protocol would work best to connect Certkiller .com with the enterprise networks it has acquired by providing scalability and VLSM support while minimizing network overhead?
A. IGRP
B. EIGRP
C. OSPF
D. RIP v2
E. RIP v1
Explanation:
RIP (both version 1 and version 2) is standards based, providing inter-operability support between vendors. RIPv2 is an enhancement to the first version and contains the following enhancements:
1. Support for variable length subnet masks (VLSM) (Because of this, RIP doesn't assume that all networks are classful.) 2. Multicast routing updates
3. Authentication with an encrypted password for routing updates
Incorrect Answers:
A, B: IGRP and EIGRP are Cisco proprietary routing protocols that are not supported by other vendors.
C: OSPF is a CPU-intensive protocol, and very large OSPF networks can experience routing and update traffic problems that seriously impact network performance. In addition, routers in large OSPF networks require large amounts of memory.
E: RIPv1 does not support VLSM.
QUESTION 110:
Which one of the following commands would you enter to terminate a VTY line session?
A. close
B. disable
C. disconnect
D. suspend
E. exit
F. None of the above
Explanation:
A VTY line is a telnet session. To end a telnet session from a remote device, enter the exit or logout command.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B, C, D. These are all invalid commands.
QUESTION 91:
Certkiller .com has the following addressing scheme requirements:
-uses a Class B IP address
-currently has 60 subnets
-has a maximum of 1000 computers on any network segment
-needs to leave the fewest unused addresses in each subnet
-uses RIP v1 Which subnet mask is appropriate to use in this network?
A. 255.255.252.0
B. 255.255.248.0
C. 255.255.255.0
D. 255.255.255.128
E. 255.255.255.248
F. 255.255.240.0
Explanation:
A subnet mask of 255.255.255.252 (/22) will result in 6 bits for the network portion and 10 bits for the host portion. This will allow for 2^6 = 64 IP subnets (62 usable), with each one supporting 2^10 = 1024 hosts (1022 usable IP addresses). This meets the requirements of 60 subnets with 1000 maximum hosts per subnet.
QUESTION 92:
When designing OSPF networks; what is the purpose of using a hierarchical design? (Select all choices that apply)
A. To reduce the complexity of router configuration
B. To speed up convergence
C. To confine network instability to single areas of the network
D. To reduce routing overhead
E. To lower costs by replacing routers
F. To decrease latency
Explanation:
An OSPF network designed in a hierarchical fashion with different areas is used because a small change in the topology of a single area won't force every router to run the SPF algorithm. Changes in one area are limited to that area only, not to every router within the entire network. Confining the topology changes to one area reduces the overhead and speeds the convergence of the network.
Reference: CCNA Self-Study CCNA ICND exam certification Guide (Cisco Press, ISBN 1-58720-083-X) Page 194
Incorrect Answers:
A. This choice is incorrect because a hierarchical design actually adds complexity to the router configuration.
E. This is incorrect because a hierarchical design will not eliminate the need for routers.
In fact, segmenting the network into multiple areas may actually require the use of additional routers.
F. The use of a hierarchical design will in no way reduce the latency involved. If additional routers are implemented in order to segment the network into additional areas, then the latency involved may actually increase.
QUESTION 93:

In this diagram, OSPF is used as the routing protocol between the corporate office and the offices on the left side of the diagram. An ISDN link provides connectivity from the central corporate router to the remote sales office on the right side of the diagram. Which type of route should the corporate office use to reach the router on the right side of the diagram if the overhead on the ISDN link is to be kept to a minimum?
A. A RIP route
B. An OSPF route
C. A static route
D. A default route
E. A dynamic route
F. None of the above
Explanation:
A static route uses the least amount of overhead because no routing protocol information will be exchanged over the ISDN link. As long as the ISDN link is up, the static route will always remain in the routing table of the corporate router.
Incorrect Answers:
A. This will not only provide additional overhead on the ISDN link as the RIP information is passed from one side to the other, but it will add additional overhead and complexity to the corporate router because now two routing protocols will need to be running. With this choice, RIP and OSPF will need to be configured on the corporate router.
B. This will add the overhead of LSP information being passed between the two routers over the ISDN link.
D. Although a default route can be a type of static route, in this case a default route will be a poor choice because then traffic destined to the Internet will go to remote office on the right side, instead of towards the ISP on the left.
E. All dynamic routing protocols will add some level of overhead. Static routes will not increase the traffic level at all over the ISDN link.
QUESTION 94:
You are a network administrator and you need to implement a routing protocol on your network that provides:
* Scalability
* VLSM support
* Minimal overhead
* Support for connecting networks using routers of multiple vendors Which of the following routing protocol would best serve your needs?
A. VTP
B. RIP version 1
C. EIGRP
D. OSPF
E. IGRP
F. CDP
Explanation:
Since one of the requirements is that the routing protocol must support other vendors, our only choices are RIP and OSPF. Since RIP version 1 does not support VLSM, OSPF is the only choice.
Incorrect Answers:
A. VTP is the VLAN Trunking Protocol. This is not a routing protocol.
B. RIP version one does not support VLSM. Note that RIPv2 does support VLSM, and would be a valid choice.
C, E: EIGRP and IGRP are Cisco proprietary routing protocols, and are not supported by other vendors.
F. CDP is the Cisco Discovery Protocol, which is used to exchange information between Cisco devices. It can only be used between Cisco routers and switches, and it is not a routing protocol.
QUESTION 95:
You need to configure a single router into load balancing traffic across 4 unequal cost paths. Which routing protocols can satisfy this requirement? (Select two)
A. RIP v1
B. RIP v2
C. IGRP
D. EIGRP
E. OSPF
F. IS-IS
Explanation:
In general, load balancing is the capability of a router to distribute traffic over all its network ports that are the same distance from the destination address. Load balancing increases the utilization of network segments, thus increasing effective network bandwidth. There are two types of load balancing: equal cost path and unequal cost path. Every routing protocol supports equal cost path load balancing. In addition to that, IGRP and EIGRP also support unequal cost path load balancing, which is known as variance. The variance command instructs the router to include routes with a metric less than n times the minimum metric route for that destination, where n is the number specified by the variance command. The variable n can take a value between 1 and 128, with the default being 1, which means equal cost load balancing (variance
Traffic is also distributed proportionally among unequal cost links, with respect to the metric.
QUESTION 96:
You need to choose a routing protocol for a new Certkiller network. This network will be running IP, IPX, and Appletalk, and you wish to utilize only one routing protocol. Which one would be the best choice?
A. OSPF
B. EIGRP
C. RIP v2
D. IGRP
E. RIP v1
Explanation:
Only EIGRP provides routing protocol support for IP, IPX, and Appletalk networks.
QUESTION 97:
Which of the routing protocols shown below support both VLSM and route summarization? (Select three)
A. IGRP
B. EIGRP
C. RIP v1
D. RIP v2
E. OSPF
F. VTP
G. CDP
Explanation:
EIGRP and OSPF support Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSM) and provide for both automatic and manual route summarization configurations. RIPv2 is an enhanced version of RIP, and overcame some of the limitations of RIP by introducing support for VLSM.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: IGRP and RIP are relatively old and simplistic routing protocols that were developed before the concepts of VLSM and route summarization.
F. VTP is the VLAN Trunking Protocol, used in switched LAN environments to carry VLAN information. It is not a routing protocol.
G. CDP is the Cisco Discovery Protocol, used between neighboring Cisco devices to automatically discover information. It is not a routing protocol.
QUESTION 98:
Which of the following routing protocols support the use of VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking)? (Select three)
A. RIPv1
B. EIGRP
C. OSPF
D. IGRP
E. RIPv2
Explanation:
Static routing, OSPF, IS-IS, EIGRP, BGP, and RIP version 2 all support VLSM.
Incorrect Answers:
A, D: RIPv1 and IGRP do not support VLSM.
Reference: Sybex CCNA Study Guide edition 4, Page 123
QUESTION 99:
Which of the following routing protocols do NOT support VLSM (variable length subnet masking)? (Choose all that apply).
A. RIPv1
B. IGRP
C. EIGRP
D. OSPF
E. IS-IS
F. RIPv2
Explanation:
RIP version 1 and IGRP are classful IP routing protocols. They do not support variable length subnet masks. Incorrect Answers:
C, D, E, F. Static routing, OSPF, IS-IS, EIGRP, BGP, and RIP version 2 all support
VLSM.
QUESTION 100:
You need to implement the use of a routing protocol that meets the following requirements:
1. Converges quickly
2. Supports VLSM, CIDR, IP, and IPX.
3. Uses minimal bandwidth for routing updates.
Which one of the following routing protocols would be the best choice?
A. RIPv1
B. RIPv2
C. IGRP
D. OSPF
E. EIGRP
Explanation:
EIGRP would be the best choice as it provides support for VLSM and CIDR, has faster convergence times than other protocols, is scalable, and supports IP, IPX, and Appletalk.
EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary routing protocol, so it will not work with other vendors.
However, the requirements of the question made no mention of the use of non-Cisco routers, so it will not be an issue in this case.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: Both of these routing protocols do not support VLSM.
B. While RIPv2 supports VLSM, it provides no support for IPX. The IPX RIP protocol is similar in function to RIP version 1. Both versions of RIP also consume more bandwidth than EIGRP.
D. OSPF does not support IPX.
QUESTION 81:
The network 172.25.0.0 has been divided into eight equal subnets. Which of the following IP addresses can be assigned to hosts in the third subnet if the ip subnet-zero command is configured on the router? (Choose three)
A. 172.25.78.243
B. 172.25.98.16
C. 172.25.72.0
D. 172.25.94.255
E. 172.25.96.17
F. 172.25.100.16
Explanation:
If we divide the address 172.25.0.0 in 8 subnets, the resulting subnets will be
1. 172.25.0.0
2. 172.25.32.0
3. 172.25.64.0 This is the third subnet
4. 172.25.96.0
5. 172.25.128.0
6. 172.25.160.0
7. 172.25.192.0
8. 172.25.224.0
Addresses that fall in the 3rd subnet will be from 172.25.64.0 ---- 172.25.95.255
Choices A, C and D lie in this network range.
QUESTION 82:
DRAG DROP
Certkiller has three locations and has plans to redesign the network accordingly. The networking team received 192.168.199.0 to use as the addressing for entire network from the administrator. After subnetting the address, the team is ready to assign the address.
The administrator plans to configure ip subnet-zero and use RIP v2 as the routing protocol. As a member of the networking team, you must address the network and at the same time converse unused addresses for future growth.
Being mindful of these goals, drag the host addresses on the left to the correct router interface. One of the routers is partially configured. Move the mouse over a router to view its configuration (** This information is missing**). Not all of the host
Answer:
QUESTION 83:
DRAG DROP
Certkiller has three locations and has plans to redesign the network accordingly. The networking team received 192.168.197.0 to use as the addressing for entire network from the administrator. After subnetting the address, the team is ready to assign the address.
The administrator plans to configure ip subnet-zero and use RIP v2 as the routing protocol. As a member of the networking team, you must address the network and at the same time converse unused addresses for future growth.
Being mindful of these goals, drag the host addresses on the left to the correct router interface. One of the routers is partially configured. Move the mouse over a router to view its configuration (** This information is missing**). Not all of the host addresses on the left will be used.
Answer:
QUESTION 84:
DRAG DROP
Certkiller has three locations and has plans to redesign the network accordingly. The networking team received 192.168.15.0 to use as the addressing for entire network from the administrator. After subnetting the address, the team is ready to assign the address.
The administrator plans to configure ip subnet-zero and use RIP v2 as the routing protocol. As a member of the networking team, you must address the network and at the same time converse unused addresses for future growth.
Being mindful of these goals, drag the host addresses on the left to the correct router interface. One of the routers is partially configured. Move the mouse over a router to view its configuration (** This information is missing**). Not all of the host addresses on the left will be used.
Answer:
Exhibit:
Please study the exhibit carefully. All of the routers in the Certkiller network are configured with the "ip subnet-zero" command. Which network addresses should be used for Link A and Network A? (Choose two) Exhibit:

A. Link A - 172.16.3.0/30
B. Link A - 172.16.3.40/30
C. Network A - 172.16.3.128/25
D. Link A - 172.16.3.112/30
E. Network A - 172.16.3.48/26
F. Network A - 172.16.3.192/26
Explanation:
If a network address is subnetted, the first subnet obtained after subnetting the network address is called subnet zero.
Consider a Class B address, 172.16.0.0. By default the Class B address 172.16.0.0 has 16 bits reserved for representing the host portion, thus allowing 65534 (216-2) valid host addresses. If network 172.16.0.0/16 is subnetted by borrowing three bits from the host portion, eight (23) subnets are obtained. The table below is an example showing the subnets obtained by subnetting the address 172.16.0.0, the resulting subnet mask, the corresponding broadcast addresses, and the range of valid host addresses.
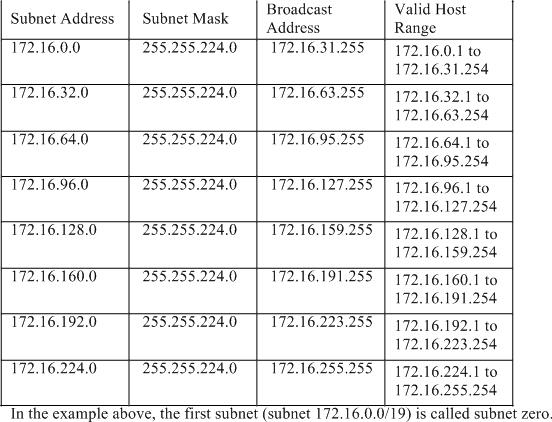
The class of the network subnetted and the number of subnets obtained after subnetting have no role in determining subnet zero. It is the first subnet obtained when subnetting the network address. Also, when you write the binary equivalent of the subnet zero address, all the subnet bits (bits 17, 18, and 19 in this case) are zeros. Subnet zero is also known as the all-zeros subnet.
In this example, link A will use the zero subnet of 172.16.30./30, while network A will need a /25 to support the 120 hosts. Answer C will support up to 128 (126 usable) hosts while options E and F will only support 62 usable IP addresses.
QUESTION 86:
A new subnet with 60 hosts has been added to the Certkiller network shown below.
Which subnet address should this network use to provide enough usable addresses while wasting the fewest addresses?
Exhibit:

A. 192.168.1.56/27
B. 192.168.1.64/26
C. 192.168.1.56/26
D. 192.168.1.64/27
Explanation:
A subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 (/26) will be needed to support 60 hosts. Option B will allow for this number of hosts, and the next available IP subnet in the 192.168.1.0 subnet that is not already used in the network is 192.168.1.64.
Incorrect Answers:
A, D: A /27 subnet mask will only support up to 30 hosts.
C: This network will conflict with the 192.168.1.48/28 network that is already in use, as the range of IP addresses used in this network is 192.168.1.48-192.168.1.63.
QUESTION 87:
In the Certkiller network shown below, which subnet address could a network administrator use for Network A on the left?
Exhibit:

A. 192.168.35.64/26
B. 192.168.35.32/27
C. 192.168.35.128/26
D. 192.168.35.192/27
E. 192.168.35.96/27
Explanation:
In order to support 62 hosts, a /26 will be needed, leaving only options A and C. The IP network in option A will conflict with the 192.168.35.64/28 that is already in use, leaving only choice C as the correct answer.
Incorrect Answers:
A: This will conflict with a network that is already in use, causing there to be duplicate IP addresses assigned in the network.
B, D, E: A /27 will only support 30 hosts.
QUESTION 88:
The Certkiller network administrator has designed the IP scheme as shown in the diagram below. What effect will this addressing scheme have on the network?
Exhibit:

A. IP traffic between subnet A and B will be prevented.
B. Routing information will not be exchanged.
C. The addressing scheme will allow all IP traffic between the LANs.
D. IP traffic between all the LANs will be prevented.
Explanation:
This scheme will allow for communication between all networks, and uses all IP addresses in the 192.168.1.0/24 IP network with no overlap. Note that RIPv2 is being used instead of RIPv1. RIPv2 carries subnet mask information allowing for VLSM networks like the one shown here.
QUESTION 89:
The network with the IP address 172.31.0.0/19 is to be configured on the Certkiller router with the partial configuration shown in the graphic. Which of the following statements describes the number of available subnets and hosts that will result from this configuration?

A. There are 7 usable subnets, with 2046 usable host addresses.
B. There are 8 usable subnets, with 30 usable host addresses.
C. There are 7 usable subnets, with 30 usable host addresses.
D. There are 8 usable subnets, with 2046 usable host addresses.
E. There are 7 usable subnets, with 8190 usable host addresses.
F. There are 8 usable subnets, with 8190 usable host addresses.
Explanation:
The 172.31.0.0/19 will have 3 bits in the network portion, and 13 bits in the host portion.
This will allow for 2^3 = 8 networks and 2^13 = 8192 hosts available for each network (8190 usable). Since the IP subnet-zero command is used the first network is available, making choice F correct.
QUESTION 90:
A new subnet with 12 hosts in the Certkiller network has been added. Which subnet address should this network use to provide enough useable addresses while wasting the fewest addresses?
Exhibit:

A. 192.168.10.80/29
B. 192.168.10.96/28
C. 192.168.10.80/28
D. 192.168.10.96/29
Explanation:
A /29 subnet mask will only support 6 IP hosts. A subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 (/28) will support up to 14 hosts, leaving only options B and C as viable. Option C will overlap with the existing 192.168.10.64/27 network, which will cause duplicate IP addresses to be assigned in the network.
What is the network address for a host with the IP address 201.100.5.68/28?
A. 201.100.5.0
B. 201.100.5.32
C. 201.100.5.64
D. 201.100.5.65
E. 201.100.5.31
F. 201.100.5.1
Explanation:
This is a C ip with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 the host 201.100.5.68/28 belong to the second subnet which is 201.100.5.64 this is determined by doing the following: subnets?2^4-2=14 hosts?2^4-2=14 valid subnet range?256-240=16 16+16=32,16+32=48,16+48=64,64+16=80 and so as you can see the ip 201.100.5.68 belongs to the second subnet which is.64
QUESTION 72:
Which of the following IP addresses fall into the CIDR block of 115.54.4.0/22? Select three
A. 115.54.8.32
B. 115.54.7.64
C. 115.54.6.255
D. 115.54.3.32
E. 115.54.5.128
F. 115.54.12.128
Explanation:
Given the CIDR block of 115.54.4.0 /22 the subnet mask is 255.255.252.0.
This gives us theIP address range of 115.54.4.1 to 115.54.7.254. Therefore, 115.54.5.128
(E),115.54.6.255 (C) and 115.54.7.64 (B) are correct.
QUESTION 73:
If an Ethernet port on router was assigned an IP address of 172.16.112.1/20, what is the maximum number of hosts allowed on this subnet?
A. 1024
B. 2046
C. 4094
D. 4096
E. 8190
Explanation:
Given IP address of 172.16.112.1 / 20, subnet mask: 255.255.240.0 max. num of hosts =(( 2^12) -2 ) = 4096-2 = 4094
QUESTION 74:
You work as network consultant. Your customer, Certkiller Inc, has a class C network license. Certkiller wants you to subnet the network to provide a separate subnet for each of its 5 departments. Each subnet must support at least 24 hosts.
Which network mask should you use?
A. 255.255.255.192
B. 255.255.255.224
C. 255.255.255.240
D. 255.255.255.248
E. 255.255.255.252
F. 255.255.255.254
Explanation:
The default subnet mask for class C network is 255.255.255.0. If one has to create 5 subnets, then 3 bits are required. With 3 bits we can create 6 subnets. Remaining 5 bits are used for Hosts. One can create 30 hosts using 5 bits in host field. This matches with requirement.
QUESTION 75:
Your Certkiller trainee Bob asks you what 11111001 binary is in decimal. What should you tell him?
A. 6
B. 193
C. 225
D. 241
E. 249
Explanation:
The binary number 11111001 translates to 128 + 64+32+16+8+1 = 249
QUESTION 76:
What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts on a local subnet that use the 255.255.255.224 subnet mask?
A. 14
B. 15
C. 16
D. 30
E. 31
F. 32
Explanation:
The subnet mask 255.255.255.224 means that there are 27 network bits. The remaining 5 bits are the host bits. The maximum possible combinations with 5 bits are 25 = 32. As all zero's and all one's hosts are not allowed so, maximum number of valid hosts with the mask 255.255.255.224 are 25 -2 =32-2 = 30 Hosts
QUESTION 77:
Which of the following IP addresses for the network 27.35.16.32/28 can be assigned to hosts? (Choose three)
A. 27.35.16.32
B. 27.35.16.33
C. 27.35.16.48
D. 27.35.16.47
E. 27.35.16.45
F. 27.35.16.44
Explanation: 25 26 27 /28 .128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
/28 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 network 32 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 next network 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 (which equals 48) Range of host values are:
RANGE 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
TO RANGE 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0
network is 32 the next network is 32 + 16 = 48 the range is 32 + 1 to 48 - 2.
this results in a range 33 to 46.
Incorrect Answers:
32 cannot be used it is the network; 47 cannot be used it is the broadcast.
A, C: These choices are both network addresses.
D. This is a broadcast address.
QUESTION 78:
DRAG DROP
Certkiller has three locations and has plans to redesign the network accordingly. The networking team received 192.168.236.0 to use as the addressing for entire network from the administrator. After subnetting the address, the team is ready to assign the address.
The administrator plans to configure ip subnet-zero and use RIP v2 as the routing protocol. As a member of the networking team, you must address the network and at the same time converse unused addresses for future growth.
Being mindful of these goals, drag the host addresses on the left to the correct router interface. One of the routers is partially configured. Move the mouse over a router to view its configuration (** This information is missing**). Not all of the host addresses on the left will be used.

Answer:

QUESTION 79:
DRAG DROP
Certkiller has three locations and has plans to redesign the network accordingly. The networking team received 192.168.132.0 to use as the addressing for entire network from the administrator. After subnetting the address, the team is ready to assign the address.
The administrator plans to configure ip subnet-zero and use RIP v2 as the routing protocol. As a member of the networking team, you must address the network and at the same time converse unused addresses for future growth.
Being mindful of these goals, drag the host addresses on the left to the correct router interface. One of the routers is partially configured. Move the mouse over a router to view its configuration (** This information is missing**). Not all of the host addresses on the left will be used.

Answer:

QUESTION 80:
In network that support VLSM, which network mask should be used for point-to-point WAN links in order to reduce waste of IP addresses?
A. /24
B. /30
C. /27
D. /26
E. /32
Explanation:
A 30-bit mask is used to create subnets with two valid host addresses. This is the exact number needed for a point-to-point connection.
QUESTION 61:
You have a network that supports VLSM and you need to reduce IP address waste in your point to point WAN links. Which of the masks below would you use?
A. /38
B. /30
C. /27
D. /23
E. /18
F. /32
Explanation:
For a single point to point link, only 2 IP addresses are required, one for the serial interface of the router at each end. Therefore, the 255.255.255.252 subnet mask is often used for these types of links because no IP addresses are wasted. The subnet mask 255.255.255.252 is a /30, so answer B is correct.
Incorrect Answers:
A. The largest mask that can be used is the single IP host mask, which is /32. It is not possible to use a /38 mask, unless of course IPv6 is being used.
C, D, E. These masks will provide for a larger number of host addresses, and since only 2
IP addresses are needed for a point to point link, these extra addresses are wasted.
F: No available host addresses with a /32 mask
QUESTION 62:
How would you express the binary number: 10101010 in its decimal and hexadecimal forms?
A. Decimal=160, hexadecimal=00
B. Decimal=170, hexadecimal=AA
C. Decimal=180, hexadecimal=BB
D. Decimal=190, hexadecimal=CC
Explanation:
For the binary equivalent of 10101010 to Decimal, the answer is 128+32+8+2=170.
For the hexadecimal number, we need to break up the binary number into two bytes of 1010 and 1010. Each one in binary is then 10 and 10, which is A and A in hexadecimal.
QUESTION 63:
Which of the following IP hosts would be valid for PC users, assuming that a /27 network mask was used for all of the networks? (Choose all that apply.)
A. 15.234.118.63
B. 83.121.178.93
C. 134.178.18.56
D. 192.168.19.37
E. 201.45.116.159
F. 217.63.12.192
Explanation:
With a 255.255.255.224 network mask, the network boundaries will be a multiple of 32, so any network will have a multiple of 32 (32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224) in the last octet. If we subtract 1 from each of these numbers (so we have 31, 63, 95, etc), we know that any IP address ending in any of these numbers will be a broadcast address.
Valid Address Current host range 83.121.178.93 83.121.178.65 to 82.121.178.94 134.178.18.56 134.178.18.33 to 134.178.18.62 192.168.19.37 192.168.19.33 to 192.168.19.62
Incorrect Answers:
A. This is the broadcast address for the 15.234.118.32/27 network.
E. This is the broadcast address for the 201.45.116.128/27 network.
F. This is the network address for the 217.63.12.192/27 network.
QUESTION 64:
You are the network administrator at Certkiller . Certkiller has been provided with the network address 165.100.27.0/24. The Certkiller CEO wants to know how many subnetworks this address provides, and how many hosts can be supported on each subnet.
What would your reply be? (Choose all that apply)
A. One network with 254 hosts.
B. 254 networks with 254 hosts per network.
C. 65,534 networks with 255 hosts per network.
D. 30 networks with 64 hosts per network.
E. 254 networks with 65,534 per network.
When we have address 165.100.27.0/24 the number of networks is 1 with 254 hosts because this address is already subnetted and valid hosts range are 165.100.27.1-165.100.27.254, making the right answer
A. If the address was
165.100.0.0/24 then right answer is B.
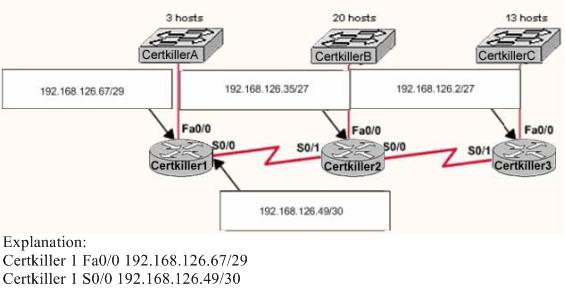
QUESTION 65:
DRAG DROP
Certkiller has three locations and has plans to redesign the network accordingly. The networking team received 192.168.126.0 to use as the addressing for entire network from the administrator. After subnetting the address, the team is ready to assign the address.
The administrator plans to configure ip subnet-zero and use RIP v2 as the routing protocol. As a member of the networking team, you must address the network and at the same time converse unused addresses for future growth.
Being mindful of these goals, drag the host addresses on the left to the correct router interface. One of the routers is partially configured. Move the mouse over a router to view its configuration (** This information is missing**). Not all of the host addresses on the left will be used.
Answer:
Certkiller 2 Fa0/0 and Certkiller 3 Fa0/0 both can have either of the following 192.168.126.35/27 or 192.168.126.2/27
QUESTION 66:
The Certkiller network has been divided into 5 separate departments as displayed below:
Using a Class C IP network, which subnet mask will provide one usable subnet per department while allowing enough usable host addresses for each department specified in the graphic?
A. 255.255.255.0
B. 255.255.255.192
C. 255.255.255.224
D. 255.255.255.240
E. 255.255.255.248
F. 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
Choice C will provide for 8 separate subnets with 30 usable hosts per subnet. Since we only require 5 different subnets with at most 16 users, this will suffice.
Incorrect Answers:
A. This will only provide 1 network with 254 hosts. This question requires 5 different networks.
B. This will only provide 4 networks, with 62 hosts per network.
D. This will provide for 14 networks, but with only 14 hosts per network so there will not be enough hosts for the Production and Engineering LANs.
E. This will provide for 62 different networks, but each with only 2 usable hosts per network.
QUESTION 67:
DRAG DROP
Certkiller has three locations and has plans to redesign the network accordingly. The networking team received 192.168.55.0 to use as the addressing for entire network from the administrator. After subnetting the address, the team is ready to assign the address.
The administrator plans to configure ip subnet-zero and use RIP v2 as the routing protocol. As a member of the networking team, you must address the network and at the same time converse unused addresses for future growth.
Being mindful of these goals, drag the host addresses on the left to the correct router interface. One of the routers is partially configured. Not all of the host addresses on the left will be used.
Answer:
QUESTION 68:
You are the network administrator at Certkiller . Certkiller has been assigned the class C IP address 189.66.1.0 by its Internet Service Provider. If you divide the network range by using the 255.255.255.224 subnet mask, how many hosts can be supported on each network?
A. 14
B. 16
C. 30
D. 32
E. 62
F. 64
Explanation:
The subnet mask 255.255.255.224 is a 27 bit mask (11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000). It uses 3 bits from the host Id for the network ID, leaving 5 bits for host addresses. We can calculate the number of hosts supported by this subnet by using the 2n-2 formula where n represents the number of host bits. In this case it will be 5. 25-2 gives us 30.
Incorrect Answers:
A. Subnet mask 255.255.255.240 will give us 14 host addresses.
B. Subnet mask 255.255.255.240 will give us a total of 16 addresses. However, we must still subtract two addresses (the network address and the broadcast address) to determine the maximum number of hosts the subnet will support.
D. Subnet mask 255.255.255.224 will give us a total of 32 addresses. However, we must still subtract two addresses (the network address and the broadcast address) to determine the maximum number of hosts the subnet will support.
E. Subnet mask 255.255.255.192 will give us 62 host addresses.
F. Subnet mask 255.255.255.192 will give us a total of 64 addresses. However, we must still subtract two addresses (the network address and the broadcast address) to determine the maximum number of hosts the subnet will support.
QUESTION 69:
Which of the following statements are true regarding a network using a subnet mask of 255.255.248.0? (Choose three)
A. It corresponds to a Class A address with 13 bits borrowed.
B. It corresponds to a Class B address with 4 bits borrowed.
C. The network address of the last subnet will have 248 in the 3rd octet.
D. The first 21 bits make the host portion of the address.
E. This subnet mask allows for 16 total subnets to be created.
F. The subnetwork numbers will be in multiples of 8.
Explanation:
This subnet mask includes the first 5 bits within the third octet, so for a class A address 13 bits will be used for the mask (8 bits in the second octet plus 5 in the third).
Since the first 5 bits are used in this octet, that means that remaining 3 bits in this octet will be available for hosts, so each network will be a factor of 8, making the last available subnet with a .248 in the third octet.
QUESTION 70:
Which of the following IP addresses is a private IP address? Select all that apply.
A. 12.0.0.1
B. 168.172.19.39
C. 172.20.14.36
D. 172.33.194.30
E. 192.168.42.34
Explanation:
RFC 1918 Private Address Space:
QUESTION 41:
Which one of the binary bit patterns below denotes a Class B address?
A. 0xxxxxxx
B. 10xxxxxx
C. 110xxxxx
D. 1110xxxx
E. 11110xxx
Explanation:
Class B addresses start with a binary of 10. The valid class B range is 128.0.0.0-191.255.255.255.
Incorrect Answers:
A. Class A addresses start with 0, as they are addresses that are less than 128.
C. Class C addresses start with 110, for a value of 192.0.0.0-223.255.255.255
D. Class D addresses start with 1110. They are reserved for multicast use
E. Class E addresses start with 11110. They are currently reserved for experimental use.
QUESTION 42:
The Certkiller network consists of 5 different departments as shown below:
You are a systems administrator at Certkiller and you've just acquired a new Class
C IP network. Which of one of the subnet masks below is capable of providing one useful subnet for each of the above departments (support, financial, sales & development) while still allowing enough usable host addresses to meet the needs of each department?
A. 255.255.255.128
B. 255.255.255.192
C. 255.255.255.224
D. 255.255.255.240
E. 255.255.255.248
F. 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
The network currently consists of 5 subnets. We need to subnet the Class C network into at least 5 subnets. This requires that we use 3 bits for the network address. Using the formula 2n-2 we get 6. This also leaves us with 5 bits for hosts, which gives us 30 hosts.
Incorrect Answers:
A. Only 1 bit is required to give us 128 but 1 bit gives us 0 subnets.
2 bits are required to give us 192 but 2 bits gives us only 2 subnets. This is too few.
D. 4 bits are required to give us 240. This gives us 14 subnets. However we are left with 4 bits for hosts leaving us with 14 host addresses. Two of the networks require more than 14 hosts so this will not do.
E. 5 bits are required to give us 248. This gives us 30 subnets. However we are left with 3 bits for hosts leaving us with 6 host addresses. All the networks require more than 6 hosts so this will not do.
F. 6 bits are required to give us 252. This gives us 62 subnets. However we are left with 2 bits for hosts leaving us with 2 host addresses. This is too few.
QUESTION 43:
Your network uses the172.12.0.0 class B address. You need to support 459 hosts per subnet, while accommodating the maximum number of subnets. Which mask would you use?
A. 255.255.0.0.
B. 255.255.128.0.
C. 255.255.224.0.
D. 255.255.254.0.
Explanation:
To obtain 459 hosts the number of host bits will be 9. This can support a maximum of 510 hosts. To keep 9 bits for hosts means the last bit in the 3rd octet will be 0. This gives 255.255.254.0 as the subnet mask.
QUESTION 44:
Using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.224, which of the IP addresses below can you assign to the hosts on this subnet? (Select all that apply)
A. 16.23.118.63
B. 87.45.16.159
C. 92.11.178.93
D. 134.178.18.56
E. 192.168.16.87
F. 217.168.166.192
Explanation:
Since the subnet mask is 255.255.255.224, the number of network hosts that is available is 30. Every network boundary will be a multiple of 32. This means that every subnet will be a multiple (0, 32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224) and the broadcast address for each of these subnets will be one less this number (31, 63, 95, 127, 159, 191, 223). Therefore, any IP address that does not end in one of these numbers will be a valid host IP address.
C. Valid Host in subnetwork 2 (92.11.178.64 to 92.11.178.95)
D. Valid Host in subnetwork 1 (134.178.18.32 to 134.178.18.63)
E. Valid Host in subnetwork 2 (192.168.16.64 to 192.168.16.95)
Incorrect Answers:
A. This will be the broadcast address for the 16.23.118.32/27 network.
B. This will be the broadcast address for the 87.45.16.128/27 network
F. This will be the network address for the 217.168.166.192/27 network.
QUESTION 45:
Your ISP has assigned you the following IP address and subnet mask:
IP address: 199.141.27.0
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.240
Which of the following addresses can be allocated to hosts on the resulting subnet?
(Select all that apply)
A. 199.141.27.2
B. 199.141.27.175
C. 199.141.27.13
D. 199.141.27.11
E. 199.141.27.208
F. 199.141.27.112
Explanation:
IP address = 11001000.10001101.00011011.00000000 = 199.141.27.0
Subnet mask = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000 = 255.255.255.240
Subnet # = 11001000.10001101.00011011.00000000 = 199.141.27.0
Broadcast = 11001000.10001101.00011011.00001111 = 199.141.27.15
The valid IP address range = 199.141.27.1 - 199.141.27.14
QUESTION 46:
The IP network 210.106.14.0 is subnetted using a /24 mask. How many usable networks and host addresses can be obtained from this?
A. 1 network with 254 hosts
B. 4 networks with 128 hosts
C. 2 networks with 24 hosts
D. 6 networks with 64 hosts
E. 8 networks with 36 hosts
Explanation:
A subnet with 24 bits on would be 255.255.255.0. Since this is a class C network, this subnet can have only 1 network and 254 usable hosts.
QUESTION 47:
Given that you have a class B IP address network range, which of the subnet masks below will allow for 100 subnets with 500 usable host addresses per subnet?
A. 255.255.0.0
B. 255.255.224.0
C. 255.255.254.0
D. 255.255.255.0
E. 255.255.255.224
Explanation:
Using the 2n-2 formula for host addresses, 29-2 = 510 host address, so a 9-bit subnet mask will provide the required number of host addresses. If these 9 bits are used for the hosts in a class B network, then the remaining 7 bits are used for the number of networks.
Again using the 2n-2 formula, we have 2n-2 = 126 networks that are available.
Incorrect Answers:
A. This will provide for only 1 network with 216-2 = 65534 hosts
B. This will provide for 6 networks with 8190 host addresses.
D. This will provide 254 networks and 254 hosts.
E. This will provide 2046 different networks, but each network will have only 30 hosts.
QUESTION 48:
You have a class C network, and you need to design it for 5 usable subnets with each subnet handling a minimum of 18 hosts each. Which of the following network masks should you use?
A. 225.225.224.0.
B. 225.225.240.0.
C. 225.225.255.0.
D. 255.255.255.224
E. 225.225.255.240
Explanation:
The default subnet mask for class C network is 255.255.255.0. If one has to create 5 subnets, then 3 bits are required. With 3 bits we can create 6 subnets. The remaining 5 bits are used for Hosts. One can create 30 hosts using 5 bits in host field. This matches with the requirement.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B: This is an illegal subnet mask for a class C network, as the third octet can not be divided when using a class C network.
C. This is the default subnet mask for a class C network. It provides for one network, with 254 usable host IP addresses.
E. This subnet mask will provide for 14 separate networks with 14 hosts each. This does not meet the requirement of a minimum of 18 hosts.
QUESTION 49:
The 213.115.77.0 network was subnetted using a /28 subnet mask. How many usable subnets and host addresses per subnet were created as a result of this?
A. 2 networks with 62 hosts
B. 6 networks with 30 hosts
C. 16 networks and 16 hosts
D. 62 networks and 2 hosts
E. 14 networks and 14 hosts
F. None of the above
Explanation:
A class C subnet with a 28 bit mask requires 4 bits for the network address, leaving 4 bits for host addresses. Using the 2n-2 formula (24-2 in this case) we have 14 host addresses and 16 network addresses.
Incorrect Answers:
A. This would be the result of a /26 network mask
B. This would be the result of a /27 network mask
C. Remember we need to always subtract two for the network and broadcast addresses, so this answer is incorrect.
D. This would be the result of a /30 network mask.
QUESTION 50:
The 201.145.32.0 network is subnetted using a /26 mask. How many networks and IP hosts per network exists using this subnet mask?
A. 4 networks with 62 hosts
B. 64 networks and 4 hosts
C. 4 networks and 62 hosts
D. 62 networks and 2 hosts
E. 6 network and 30 hosts
Explanation:
A class C network with a 26 bit mask requires 2 bits for the network address, leaving 6 bits for host addresses. Using the 2n-2 formula (22 for the network and 26-2for hosts) we have 4 network addresses and 62 host addresses.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B: This is not a possible combination. No network mask will provide for 64 usable hosts, because we must always subtract 2 for the network and broadcast address.
D. This would be the result of a /30 mask.
E. This would be the result of a /27 network mask.
You have a class B network with a 255.255.255.0 mask. Which of the statements below are true of this network? (Select all valid answers)
A. There are 254 usable subnets.
B. There are 256 usable hosts per subnet.
C. There are 50 usable subnets.
D. There are 254 usable hosts per subnet.
E. There are 24 usable hosts per subnet.
F. There is one usable network.
Explanation:
The default subnet mask for Class B is 255.255.0.0. Thus an extra 8 bits have been used for the network portion, leaving 8 for hosts. The 2n - 2 formula (28 - 2 in this case for both the network and IP hosts) gives us 254 networks and 254 hosts per network.
Incorrect Answers:
B. We must remember to always subtract 2 (one for the network, and one for the broadcast) so the result is 254, not 256.
C, E: No possible network mask would give us this exact number of subnets or hosts.
F. This would be true if this were a class C network, not a class B.
QUESTION 52:
How many usable IP addresses can you get from a conventional Class C address?
A. 128
B. 192
C. 254
D. 256
E. 510
Explanation:
Class Caddresses range from 192.0.0.0 through 223.225.225.225 and default subnet maskof 255.255.255.0. In Class C addresses, the first 24 bits are used as for the network IDwhile only the last 8 bits is used for the host ID. Using the 2n-2 formula, we can calculate that Class C addresses can support a maximum of 254 (28-2) hosts.
Incorrect Answers:
D. Note that the question asked for the number of usable addresses, and not the total number of all addresses. We must subtract 2 for the network and broadcast addresses to calculate the number of usable addresses in any subnet.
QUESTION 53:
Your ISP assigned you a full class B address space. From this, you need at least 300 sub-networks that can support at least 50 hosts each. Which of the subnet masks below are capable of satisfying your needs? (Select two).
A. 255.255.255.0
B. 255.255.255.128
C. 255.255.252.0
D. 255.255.255.224
E. 255.255.255.192
F. 255.255.248.0
Explanation:
Requirement in the question is that the company needs 300 subnets and 50 hosts per subnet.

With 9 bits used for the subnet portion, we get 510 subnets and using the remaining 7 bits for the hosts gives us 126 hosts per subnet. The subnet mask will be 255.255.255.128
With 10 bits used for the subnet portion, we get 1022 subnets and then using the remaining 6 bits for hosts provides 62 hosts per subnet. The subnet mask will be 255.255.255.192 in this case which will also fulfill the requirement.
QUESTION 54:
A Certkiller PC has the IP address 172.16.209.10 /22. What is the subnet of this address?
A. 172.16.42.0
B. 172.16.107.0
C. 172.16.208.0
D. 172.16.252.0
E. 172.16.254.0
Explanation:
172.16.209.10/22 translates to 10101100.00010000.11010001.00001010 in binary form. The network portion is 22 bits, so after the logical AND comparison the network address translates to10101100.00010000.110100001.00001010. Converting the network portion to decimal results in the address 172.16.208.0/22
QUESTION 55:
You've been assigned the CIDR (classless inter domain routing) block of 115.64.4.0/22 from your ISP. Which of the IP addresses below can you use for a host? (Select all valid answers)
A. 115.64.8.32
B. 115.64.7.64
C. 115.64.6.255
D. 115.64.3.255
E. 115.64.5.128
F. 115.64.12.128
Explanation:
115.64.4.0 = 01110011.01000000.00000100.00000000
Subnet mask = 11111111.11111111.11111100.00000000= 255.255.252.0
Subnet number = 01110011.01000000.00000100.00000000= 115.64.4.0
Broadcast = 01110011.01000000.00000111.11111111= 115.64.7.255
Valid address range = 115.64.4.1 - 115.64.7.254
QUESTION 56:
A Certkiller remote office branch is set up as shown in the diagram below:

All of the hosts in the above exhibit are connected with each other via the single Catalyst switch. Which of the following statements correctly describe the addressing scheme of this network? (Select three)
A. The subnet mask in use is 255.255.255.192.
B. The subnet mask in use is 255.255.255.128.
C. The IP address 172.16.1.25 can be assigned to hosts in VLAN1.
D. The IP address 172.16.1.205 can be assigned to hosts in VLAN1
E. The LAN interface of the router is configured with one IP address.
F. The LAN interface of the router is configured with multiple IP addresses.
Explanation:
Based on the diagram above, the subnet mask used for each VLAN is 255.255.255.128.
This means that hosts in VLAN 1 will be addressed 172.16.1.1-172.16.1.126, with
172.16.1.127 being used as the broadcast address. Hosts in VLAN 2 will be addressed
172.16.1.129-172.16.1.254. Because there is only one LAN interface on the router, sub interfaces will be used, so the router's LAN interface will be configured with 2 IP addresses, one for VLAN 1 and 1 for VLAN 2.
Incorrect Answers:
A. This subnet mask will only provide 62 host IP addresses, and the diagram shows that as many as 114 host IP addresses are needed.
D. This IP address can be used in VLAN 2, not VLAN 1.
E. Since there are 2 subnets in this network, each separate network will require a distinct default gateway IP address, so 2 IP addresses will be required on the LAN interface of the router.
QUESTION 57:

(Select three)
A. 172.16.82.255
B. 172.16.95.255
C. 172.16.64.255
D. 172.16.32.255
E. 172.16.47.255
F. 172.16.79.255
Explanation:
The subnets in the network are subnetted Class B addresses. A /20 subnet mask means that the subnet addresses increment by a factor of 16. For example: 172.16.16.0, 172.16.32.0, 172.16.48.0, 172.16.64.0 etc. The broadcast address is the last IP address before the next subnet address.
B. The switch IP address (172.16.82.90) is in the 172.16.80.0 subnet. 172.16.95.255 is the broadcast address for the 172.16.80.0 subnet.
E. This is the broadcast address for the 172.16.32.0 subnet.
F. This is the broadcast address for the 172.16.64.0 subnet.
QUESTION 58:
Which one of the following varieties of NAT utilizes different ports to map multiple IP addresses to a single globally registered IP address?
A. Static NAT
B. Port loading
C. NAT Overloading
D. Dynamic NAT
E. None of the above
Explanation:
Port address translation, or NAT overloading, uses transport layer port information to dynamically create NAT entries. This is also known as one to many network address translation.
Incorrect Answers:
A. Static NAT is known as one to one NAT, and is used to map a single IP address to a single registered IP address. It is often used for servers that need to be accessed via the Internet.
B, D: This is the incorrect term, and is not used.
QUESTION 59:
On the topic of VLSM, which one of the following statements best describes the concept of the route aggregation?
A. Deleting unusable addresses through the creation of many subnets.
B. Combining routes to multiple networks into one supernet.
C. Reclaiming unused space by means of changing the subnet size.
D. Calculating the available host addresses in the AS.
Explanation:
In the networking world route aggregate means combining routes to multiple networks into one. This is also known as route summarization or supernetting. It is normally used to reduce the number of route entries in the routing table by advertising numerous routes into one larger route.
Reference: CCNA Self-Study CCNA ICND exam certification Guide (Cisco Press,
ISBN 1-58720-083-X) Page 236.
QUESTION 60:
You have a single Class C IP address and a point-to-point serial link that you want to implement VLSM on. Which subnet mask is the most efficient?
A. 255.255.255.0
B. 255.255.255.240
C. 255.255.255.248
D. 255.255.255.252
E. 255.255.255.254
Explanation:
For a single point to point link, only 2 IP addresses are required, one for the serial interface of the router at each end. Therefore, the 255.255.255.252 subnet mask is often used for these types of links, as no IP addresses are wasted.