QUESTION 101:
See the Certkiller WAN diagram below:
Certkiller has four offices, each with its own network, as shown in the graphic. Three of the networks have approximately 50 hosts each, and one network has 10 hosts.
The multi-vendor routers are connected by serial links that use separate subnetwork numbers. The Certkiller network has leased one Class C address to be used for all networks and serial links, and they do not wish to replace any of their existing routers.
Which routing protocol would be most appropriate for this scenario?
A. TCP/IP
B. RIP version 1
C. RIP version 2
D. IGRP
E. EIGRP
F. All of the above are acceptable
Explanation:
The question describes 2 important requirements. The first is the fact that a routing protocol that supports VLSM is needed, as specified by the fact that one class C address range is to be used for all networks. The second important requirement is that routers from multiple vendors are being used, so the routing protocol chosen must be non-proprietary. RIP version 2 is a standards based routing protocol that supports variable length subnet masking (VLSM). Note that OSPF would also be a viable choice, but it was not one of the answer choices.
Incorrect Answers:
A. This is not a routing protocol.
B. RIP version 1 does not support VLSM
D, E: Although these both support VLSM, IGRP and EIGRP are Cisco proprietary routing protocols which are not supported by other router vendors.
QUESTION 102:
RIP version 2 is being used as the routing protocol within the Certkiller network.
What does RIP version 2 use to prevent routing loops? (Choose two)
A. CIDR
B. Split horizon
C. Authentication
D. Classless masking
E. Hold-down timers
F. Multicast routing updates
G. Path Vectoring
Explanation:
Distance Vector routing protocols employ the split horizon mechanism to reduce the possibility of routing loops. Split horizon blocks information about routes from being advertised by a router out of any interface from which that information originated.
RIP versions 1 and 2 also use the concept of hold timers. When a destination has become unreachable (or the metric has increased enough to cause poisoning), the destination goes into "holddown". During this state, no new path will be accepted for the same destination for this amount of time. The hold time indicates how long this state should last.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C, D, F. Although these are all features and functions of RIP version 2, they are not mechanisms used to prevent routing loops.
G. Path Vectoring is a concept used by BGP routers. RIP version 1 and 2 are considered to be distance vector routing protocols.
QUESTION 103:
The Certkiller WAN is displayed in the diagram below:
A. RIP v1
B. RIP v2
C. IGRP
D. OSPF
E. BGP
F. EIGRP
Explanation:
the exhibit showed routers withVariable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM), and asked which 3 protocols can be used. 3 protocols that support VLSM are RIP v2, OSPF and EIGRP.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: Both of these routing protocols do not support VLSM information.
E. BGP is used for external routing between different autonomous systems, and is not generally used within a single AS.
QUESTION 104:
The Certkiller Network consists of the following 5 IP networks:
NETWORK 1: 192.168.10.0/26
NETWORK 2: 192.168.10.64/27
NETWORK 3: 192.168.10.96/27
NETWORK 4: 192.168.10.128/30
NETWORK 5: 192.168.10.132/30
Which of the following routing protocols will support this IP addressing scheme?
(Choose all that apply).
A. RIP version 1
B. RIP version 2
C. IGRP
D. EIGRP
E. OSPF
F. BGP
Explanation:
Because this network is using IP subnets with variable length subnet masks, only routing protocols that support VLSM will fit this particular case. The routing protocols that support VLSM are RIP v2, EIGRP and OSPF.
Incorrect Answers:
A, C: RIP version 1 and IGRP do not support VLSM information within the routing updates.
F. BGP is used for inter-AS routing, such as the Internet. It is not normally used as an
Interior routing protocol.
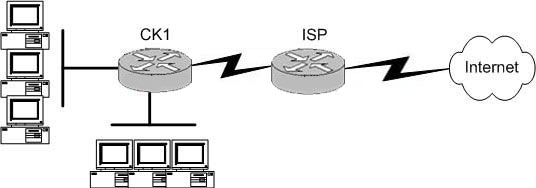
QUESTION 105:
The Certkiller network is displayed in the diagram shown below:
The Certkiller network consists of a small office with twenty-five employees that has one connection to the Internet through the CK1 router. What routing configurations are recommended on the CK1 and ISP routers?
A. BGP on both the routers.
B. RIP on both the routers.
C. Default routes on both routers.
D. BGP on the ISP router and a static route on CK1 .
E. A default route on CK1 and a static route on the ISP router.
Explanation:
Since private network use RFC 1918 IP address ranges internally, and because of security reasons, it is generally not possible to use an interior routing protocol with the ISP. This eliminates choice B. When connecting to an ISP, usually only BGP or static routes are supported. In this case, since there is only one connection to the Internet, BGP is not needed so choices A and D can be eliminated. A static default route would be needed on router CK1 to route to the Internet. In turn, the ISP only needs a specific static route to reach the LAN of the Certkiller network.
Incorrect Answers:
A, D: BGP is not needed on networks that contain only a single link to the Internet.
B. Interior routing protocols are generally not supported with an ISP.
C. A default route on the ISP router would send all of their customers Internet traffic to the Certkiller network, and not the Internet.
QUESTION 106:
What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR election?
A. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which OSPF router will become the DR or BDR in a point-to-point network
B. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which interface will be used to form a neighbor relationship with another OSPF router
C. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which router will become the DR or BDR in a multi access network
D. It is used to determine which interfaces will send Hello packets to neighboring OSPF routers
Explanation:
The router ID is the highest IP address or the highest IP address among loopback addresses (if one is configured) on the Cisco router or can be configured manually by "router-id x.x.x.x". Once the router ID is chosen, it will not be changed unless the OSPF process is reset(clear ip ospf process xx) or the router is reloaded. The IP address of router ID doesn't need to be reachable, but it is used to determine which will router will become the DR or BDR in a multi-access network.
QUESTION 107:
The Certkiller network is shown in the following exhibit:
Which routing protocols can be used within the enterprise network shown in the diagram? (Choose three.)
A. RIP v1
B. RIP v2
C. IGRP
D. OSPF
E. BGP
F. EIGRP
Explanation:
In this network there are IP subnets which use variable length subnet masks. RIP V2,
OSPF and EIGRP are the interior routing protocols that support VLSM.
QUESTION 108:
What is the advantage of using a multipoint interface instead of point-to-point subinterfaces when configuring a Frame Relay hub in a hub-and-spoke topology?
A. It avoids split-horizon issues with distance vector routing protocols.
B. IP addresses can be conserved if VLSM is not being used for subnetting.
C. A multipoint interface offers greater security compared to point-to-point subinterface configurations.
D. The multiple IP network addresses required for a multipoint interface provide greater addressing flexibility over point-to-point configurations.
Explanation:
Frame Relay supports two types of interfaces: point-to-point and multipoint. The one you choose determines whether you need to use the configuration commands that ensure IP address to data-link connection identifier (DLCI) mappings. After configuring the PVC itself, you must tell the router which PVC to use in order to reach a specific destination.
Let's look at these options:
1. Point-to-point subinterface - With point-to-point subinterfaces, each pair of routers has its own subnet. If you put the PVC on a point-to-point subinterface, the router assumes that there is only one point-to-point PVC configured on the subinterface. Therefore, any IP packets with a destination IP address in the same subnet are forwarded on this VC. This is the simplest way to configure the mapping and is therefore the recommended method.
Use the frame-relay interface-dlci command to assign a DLCI to a specified Frame
Relay subinterface.
2. Multipoint networks - Multipoint networks have three or more routers in the same subnet. If you put the PVC in a point-to-multipoint subinterface or in the main interface (which is multipoint by default), you need to either configure a static mapping or enable inverse Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) for dynamic mapping.
QUESTION 109:
Certkiller .com is merging with several local businesses that use routers from multiple vendors. Which routing protocol would work best to connect Certkiller .com with the enterprise networks it has acquired by providing scalability and VLSM support while minimizing network overhead?
A. IGRP
B. EIGRP
C. OSPF
D. RIP v2
E. RIP v1
Explanation:
RIP (both version 1 and version 2) is standards based, providing inter-operability support between vendors. RIPv2 is an enhancement to the first version and contains the following enhancements:
1. Support for variable length subnet masks (VLSM) (Because of this, RIP doesn't assume that all networks are classful.) 2. Multicast routing updates
3. Authentication with an encrypted password for routing updates
Incorrect Answers:
A, B: IGRP and EIGRP are Cisco proprietary routing protocols that are not supported by other vendors.
C: OSPF is a CPU-intensive protocol, and very large OSPF networks can experience routing and update traffic problems that seriously impact network performance. In addition, routers in large OSPF networks require large amounts of memory.
E: RIPv1 does not support VLSM.
QUESTION 110:
Which one of the following commands would you enter to terminate a VTY line session?
A. close
B. disable
C. disconnect
D. suspend
E. exit
F. None of the above
Explanation:
A VTY line is a telnet session. To end a telnet session from a remote device, enter the exit or logout command.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B, C, D. These are all invalid commands.